Dataset Classification: Difference between revisions
Mmaciejewski (talk | contribs) |
Mmaciejewski (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Datasets}} | |||
= Dataset Classification = | = Dataset Classification = | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
* Apply bulk classifications for ease of use. | * Apply bulk classifications for ease of use. | ||
* Combine classification with tags and supplemental data for rich, queryable metadata. | * Combine classification with tags and supplemental data for rich, queryable metadata. | ||
== Removing Datasets from the Archive == | |||
Users with the '''NMR Facility''' role for a given facility have additional privileges in the Classification modal. Specifically, they are presented with a special option: | |||
'''CAUTION – purge from the NAN Archive''' | |||
This option is only visible to facility managers and only for datasets collected within their own facility. When selected, the dataset is: | |||
* Immediately removed from the NAN database | |||
* Deleted from NAN file storage shortly thereafter | |||
This action is irreversible and should be used with caution. It is intended for cases where an experiment was mistakenly harvested or is otherwise unsuitable for archival in NAN. | |||
Latest revision as of 17:07, 10 June 2025
Dataset Classification
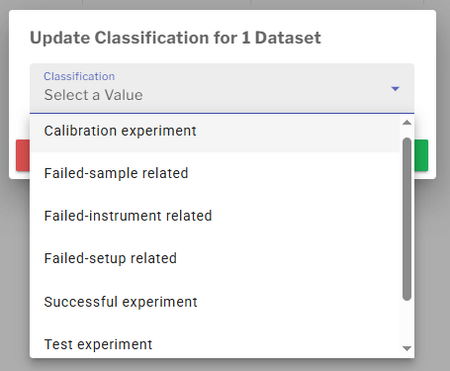
From the Data Browser, users may classify one or more datasets by selecting the Classification action from the context menu. This launches a dialog that allows the user to choose a classification from a controlled list:
- Calibration experiment
- Failed experiment due to sample-related issues
- Failed experiment due to instrument-related issues
- Failed experiment due to setup issues
- Successful experiment
- Test experiment
Classifying datasets provides a valuable layer of annotation that supports long-term data reuse and analysis. While this feature introduces a small additional burden to users, it is optimized for ease of use. Classifications can be applied in bulk, allowing entire sets of experiments to be labeled in just a few seconds.
Why Classification Matters
Dataset classification plays a central role in organizing and curating scientific data. In NAN, datasets are categorized using a combination of automated and user-defined metadata, including:
- Tags
- Pulse program
- Data harvesting method
- Dimensionality
- Experimental parameters
- Linked samples
- Supplemental data
- Redundancy status
- Classification (user-defined)
This structured metadata enables powerful filtering capabilities in the Data Browser, allowing users to rapidly identify relevant experiments based on specific criteria.
As the NAN archive continues to grow, these filters will become essential tools for researchers. In particular, classification is a key element in generating curated data collections that support:
- Machine learning model training
- Quality control benchmarking
- Comparative analysis
- Downstream automated processing workflows
By consistently applying dataset classifications, users help build a more robust and reusable data ecosystem—enabling both human and machine-driven discovery.
Best Practices
- Use the classification feature regularly, especially for test and failed experiments, to keep your dataset library clean and navigable.
- Apply bulk classifications for ease of use.
- Combine classification with tags and supplemental data for rich, queryable metadata.
Removing Datasets from the Archive
Users with the NMR Facility role for a given facility have additional privileges in the Classification modal. Specifically, they are presented with a special option:
CAUTION – purge from the NAN Archive
This option is only visible to facility managers and only for datasets collected within their own facility. When selected, the dataset is:
- Immediately removed from the NAN database
- Deleted from NAN file storage shortly thereafter
This action is irreversible and should be used with caution. It is intended for cases where an experiment was mistakenly harvested or is otherwise unsuitable for archival in NAN.